Data Science: An Introduction
The use of the term Data Science is more and more common, but what does it exactly mean?
Data science is a multidisciplinary commixture of data algorithm development, and technology inference, in order to settle analytically complex problems. The main focus was on making structure and solutions to store data. Data Science is the forthcoming of Artificial Intelligence. Therefore, it is very essential to know what is Data Science and how can it add value to your business.
Let’s Understand Why We Need Data Science
Through simple BI tools, we can analyze framed and small data. Distinct data in the traditional systems which were mostly fixed, today most of the data is unorganized. Data originate from different sources like financial logs, multimedia forms, sensors, and instruments. Simple BI tools are not able to transform this huge volume and mixture of data. This is why we require more structure and leading analytical tools and innovations for converting, evaluating and designing meaningful judgment out of it.
What is Data Science – The Essential Skill Set
Data Science is a commixture of skills in three primary areas:
- Mathematics Expertise
- Technology and Hacking
- Strong Business Acumen
Mathematics Expertise:
Mining data vision and framework of a data product is the capability to view the results through an assessable lens. There are compositions, dimensions, and interactions in data that can be conveyed methodically. Clarifications to many business problems involve building analytic models found in the tough math, where being able to accept the hidden mechanics of those models is key to progress in building them. While statistics is extensive, it is not the only type of math exercise. Through, it is helpful for data scientists to have wideness and deepness in their intelligence of mathematics.
Technology and Hacking:
Hacking – i.e., creativity and ability in using technical skills to build things and find close relation to problems.
Why is hacking ability important? Because data scientists handle technology in order to tangle excessive data sets and work with complicated algorithms, and it desires tools far more refined than Excel.
A hacker is a technical ninja, able to greatly operate their way through technical require in order-making their code work.
Strong Business Acumen:
It is necessary for a data scientist to be a diplomatic business consultant. Working so hard with data, data scientists are arranged to learn from data in ways no one else can. That builds the authority to convert conclusion to shared knowledge, and share to strategy on how to solve core business problems.
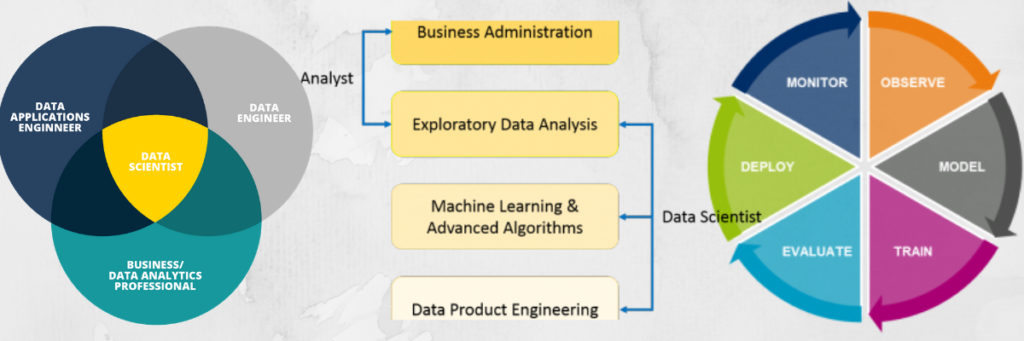
Lifecycle of Data Science
- Discovery: Before you begin the project, it is important to know the kind of specifications and terms. Here, you assess if you have the necessary reserves present in terms of population, mechanics, moment and details to support the project. In this phase, you also need to form the business problem and formulate initial hypotheses (IH) to test.
- Data Preparation: Analytical sandbox is required to execute analytics of the full projects. Further, you will implement ETLT (extract, transform, load and transform) to get data into the sandbox.
- Model Planning: Here, you will regulate the mechanism and techniques to draw the link between variables. These links will set the base for the algorithms which you will imply.
- Model Building: In this, datasets for training and testing intent will expand. You will evaluate various learning techniques like classification, association, and bundle to build the model.
- Operationalize: In this, you drop final reports, direction, code, and special records.
This will give you a clear picture of the performance and other related pressure on a small scale before full implementation.
- Communicate Results: Now it is necessary to estimate if you have been able to attain your goal that you had planned. So, in the last, you analyze all the key findings, determine if the results of the project are a benefit or a failure based on the norm developed in the plan.


